Phosphate ions are an essential component in a variety of industries, playing a critical role in agriculture, food production, water treatment, and more. These ions, primarily derived from phosphate salts, are used in fertilizers, detergents, water purification systems, and even in the manufacture of specialty chemicals. With the growing demand for phosphate-based products, setting up a phosphate ion manufacturing plant offers significant business potential. This article will explore the key considerations, production processes, market trends, and potential challenges involved in establishing such a manufacturing facility.
The Importance of Phosphate Ions
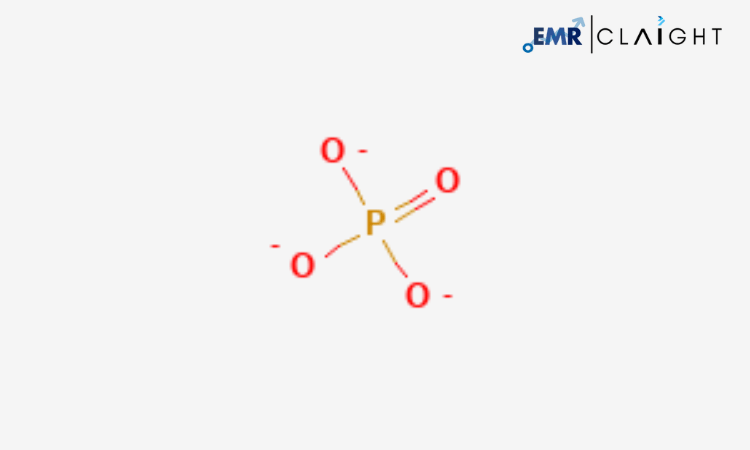
Phosphate ions (PO₄³⁻) are a fundamental part of life on Earth, as they are crucial for various biological processes, including energy transfer, cell structure, and metabolism. They are commonly found in nature as phosphate salts, and their compounds are used extensively in industrial applications. In agriculture, phosphate is a primary component of fertilizers, contributing to plant growth and ensuring food security for the global population.
Phosphates also have significant applications in industrial and consumer products. In the water treatment industry, phosphate ions are used to prevent the formation of scale in pipes and water systems. In food production, phosphates are used as preservatives and flavour enhancers. Furthermore, phosphate-based compounds are also used in detergents, as they help break down grease and dirt.
Get a Free Sample Report with Table of Contents@ https://www.expertmarketresearch.com/prefeasibility-reports/phosphate-ion-manufacturing-plant-project-report/requestsample
Market Demand for Phosphate Ions
The demand for phosphate ions is primarily driven by the need for fertilizers in agriculture. As the global population continues to grow, the demand for food production has increased significantly, leading to a higher need for fertilizers that enhance soil fertility and increase crop yields. Phosphates are a key ingredient in many commercial fertilizers, making them essential to modern farming practices.
In addition to agriculture, phosphate-based chemicals are used in a variety of industrial applications. The global phosphate market is expected to continue to grow, driven by these key sectors, alongside increasing awareness of sustainable practices in agriculture and industry. Additionally, the demand for high-quality water treatment solutions is rising, as municipalities and industries seek to improve water quality and manage resources efficiently.
Key Considerations for Setting Up a Phosphate Ion Manufacturing Plant
Starting a phosphate ion manufacturing plant requires careful planning, as there are several important factors that can influence the project’s success. These factors include sourcing raw materials, establishing an efficient production process, ensuring product quality, managing environmental concerns, and complying with regulations.
1. Location and Facility Design
The location of the manufacturing plant plays an important role in reducing production and transportation costs. It is essential to select a site with access to transportation networks, such as highways, railways, or seaports, to facilitate the smooth flow of raw materials and finished products. Proximity to raw material suppliers and key markets can also help reduce logistical challenges and improve efficiency.
Facility design should be optimized for large-scale production, with designated areas for raw material storage, chemical processing, packaging, and quality control. The plant should adhere to local building codes, safety regulations, and environmental standards. The manufacturing plant layout should also account for the flow of materials through the production process, aiming to minimize waste, ensure worker safety, and optimize operational efficiency.
2. Sourcing Raw Materials
The primary raw material for phosphate ion production is phosphate rock, which is mined in various parts of the world. Countries such as China, Morocco, and the United States are significant producers of phosphate rock. In addition to phosphate rock, other raw materials like sulfuric acid, ammonia, or sodium carbonate may be needed, depending on the specific production method and the end product.
It is essential to secure a steady, reliable supply of high-quality raw materials. Establishing partnerships with trusted suppliers and ensuring a consistent supply chain will be critical to maintaining production efficiency and meeting customer demand. Additionally, manufacturers should consider the environmental impact of raw material extraction and explore sustainable sourcing options where possible.
3. Production Process
The production of phosphate ions typically involves the extraction of phosphate from phosphate rock, followed by a series of chemical reactions to produce different phosphate compounds. These compounds can then be further processed into various forms, including phosphate salts, fertilizers, and other products. Below are some key stages in the phosphate ion production process:
-
Extraction of Phosphate: Phosphate rock is mined from the earth and processed to extract the phosphorus content. This often involves crushing and grinding the rock to release the phosphate.
-
Chemical Reactions: The phosphate extracted from the rock may undergo chemical reactions, often involving sulfuric acid or other agents, to create various phosphate compounds, including phosphoric acid or ammonium phosphate.
-
Purification: To ensure high-quality phosphate products, the extracted compounds may undergo purification processes to remove impurities and achieve the desired purity levels.
-
Granulation or Powdering: Depending on the end product, the phosphate ions may be granulated into solid particles or processed into a fine powder suitable for use in fertilizers, detergents, or other applications.
-
Packaging: Once the phosphate ions or phosphate compounds are produced, they are packaged for distribution. Packaging must be done in such a way that it protects the product from contamination, moisture, and other environmental factors that could affect quality.
4. Quality Control
Ensuring the consistency and purity of phosphate ions is crucial for meeting industry standards and customer expectations. Implementing a robust quality control system throughout the production process will help identify and eliminate defects or contaminants.
At various stages of production, testing should be conducted to monitor the quality of the raw materials, the chemical reactions, and the final product. Quality control processes may include testing for purity, particle size, solubility, and other characteristics relevant to the intended use of the phosphate product.
5. Environmental and Safety Considerations
The production of phosphate ions and phosphate-based products can have significant environmental and safety implications. Phosphate mining and processing can result in the release of hazardous substances, such as dust, sulfuric acid, and heavy metals, which must be managed carefully to prevent contamination of the air, water, and soil.
To minimize environmental impact, manufacturers should implement best practices in waste management, air filtration, and water treatment. Additionally, the use of sustainable production methods, such as recycling waste materials or exploring alternative, less harmful raw materials, can help reduce the environmental footprint of the manufacturing process.
Safety regulations should be strictly followed to ensure the well-being of workers and prevent accidents. This includes providing appropriate protective equipment, training staff on handling hazardous materials, and conducting regular safety audits.
6. Regulatory Compliance
The phosphate ion manufacturing process is subject to a variety of local and international regulations, including environmental, health, and safety standards. These regulations are put in place to protect workers, consumers, and the environment from potential risks associated with phosphate production.
Before starting production, it is essential to thoroughly understand the regulations in the target market and obtain the necessary permits and certifications. This may include certifications related to food safety, product quality, and environmental sustainability. Adhering to these regulations is critical not only for legal compliance but also for building consumer trust and ensuring long-term success in the market.
Market Trends and Potential
The demand for phosphate ions is expected to remain strong due to their key role in agriculture and various industrial applications. As the world continues to grapple with food security challenges and the need for sustainable agriculture, the demand for high-quality fertilizers will increase, driving the growth of the phosphate industry. Similarly, the continued urbanization and industrialization in emerging markets are likely to increase the need for phosphate-based water treatment solutions and detergents.
Moreover, with growing concerns about environmental sustainability, there is an increasing emphasis on reducing the environmental impact of phosphate mining and processing. This has led to innovations in sustainable manufacturing processes and the development of more eco-friendly phosphate-based products.
The phosphate market presents a promising opportunity for manufacturers who can navigate these trends and provide high-quality, sustainable products that meet the evolving needs of industries and consumers worldwide.





Leave a Reply